Method
A 3-step process starting with an extensive literature review, qualitative coding to analyze the collected data and finally a heuristic analysis of the identified mental health chatbots.
Literature Survey
We identified numerous papers centered around mental health chatbots. We focused on papers that were either explicitly discussing general design guidelines and ethical issues when designing chatbots for mental healthcare, while others were discussing best practices when designing chabots for specific usecases such as depression, mental healthcare for elderly etc. To supplement our findings, we analyzed news articles summarizing user feedback from various studies. The complete list of papers reviewed can be found here.
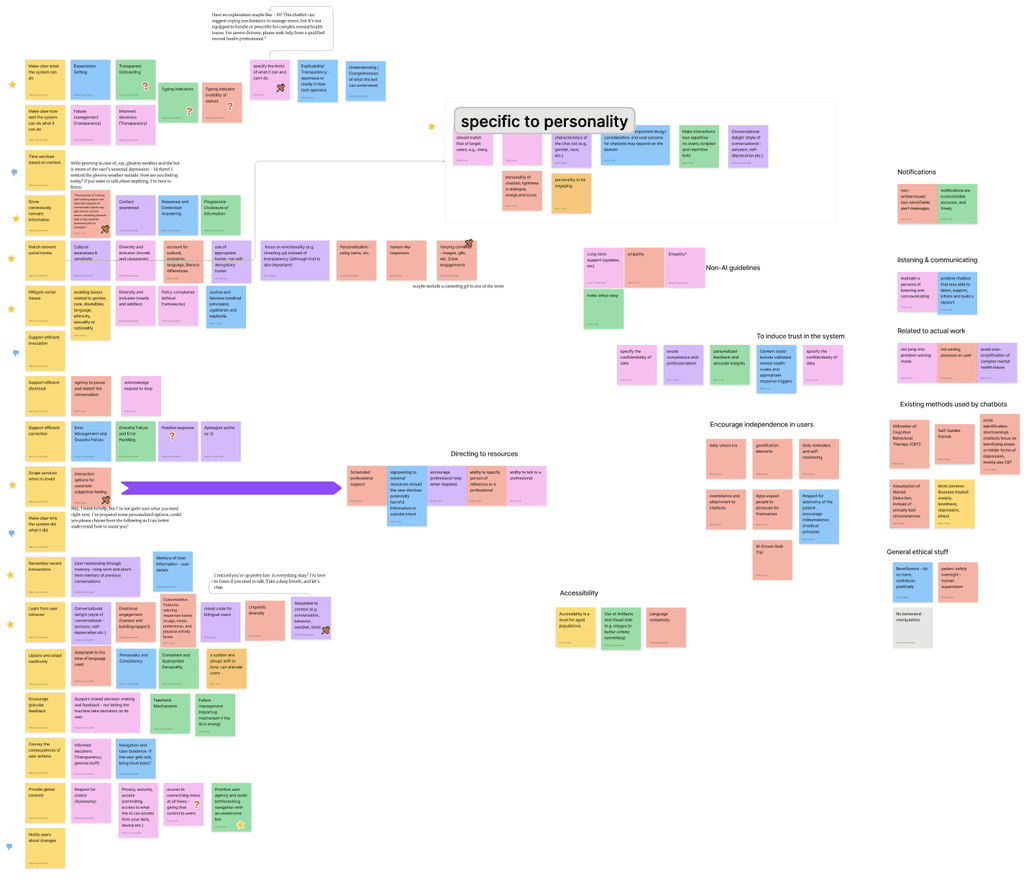
We then used qualitative analysis to extract themes alluding to Human-AI interaction since potential design guidelines are often not presented explicitly as such. After extracting approximately 100+ themes, we used closed coding to group them into categories created by Microsoft's HAI guidelines. The latter was chosen because it stands to be the most detailed and exhaustive work in capturing a variety of scenarios in Human-AI interaction.
Out of the 19 Microsoft HAI guidelines, we found that 4 were not applicable for this use-case. Additionally, we formulated 1 new guideline regarding chatbot personality, which we deemed relevant and unique to our study.
Heuristic Analysis
We selected 12 popular mental healthcare mobile apps from the PlayStore, focusing on those offering therapy chatbot services. Out of these, 5 were shortlisted for our study.
Apps such as Anima and Antar, while popular, were not included as they primarily focus on providing companionship and journaling features rather than therapeutic resources.
Similarly, apps like Woebot and Ginger by Headspace were not included due to limitations in accessing free services. The final list of shortlisted apps is as follows:

Wysa
Mental Health Support

Youper
AI For Mental Health Care

VOS.Health
Mental Health App

Audyn
AI Mental Health

Sintelly
CBT Therapy Chatbot
Case Studies
Limitations
Difficulty in creating testing scenarios
During the heuristic analysis phase, we encountered challenges in effectively engineering scenarios to test the adherence of the apps to the guidelines. The nature of the conversations, which often encompass nuanced aspects of the human psyche, made it difficult to construct scenarios that could reliably evaluate the apps' compliance. As a result, the assessment of adherence to the guidelines may not fully capture the complexities of real-world interactions with the apps.
Barriers to access
A third limitation arose from barriers to access, as some of the apps we studied restrict usage and the number of texts that can be sent on their free trial versions. This limitation added complexity to our analysis, as it limited our ability to fully explore the apps' functionalities and interactions.
Analysis without the supervision of an expert
Another limitation we faced was the lack of time and resources to consult with experts and professionals to validate the accuracy of the prompts we created and, consequently, the responses generated by the chatbot. This limitation could potentially affect the reliability of our findings, as expert input could have provided valuable insights and validation of our approach.